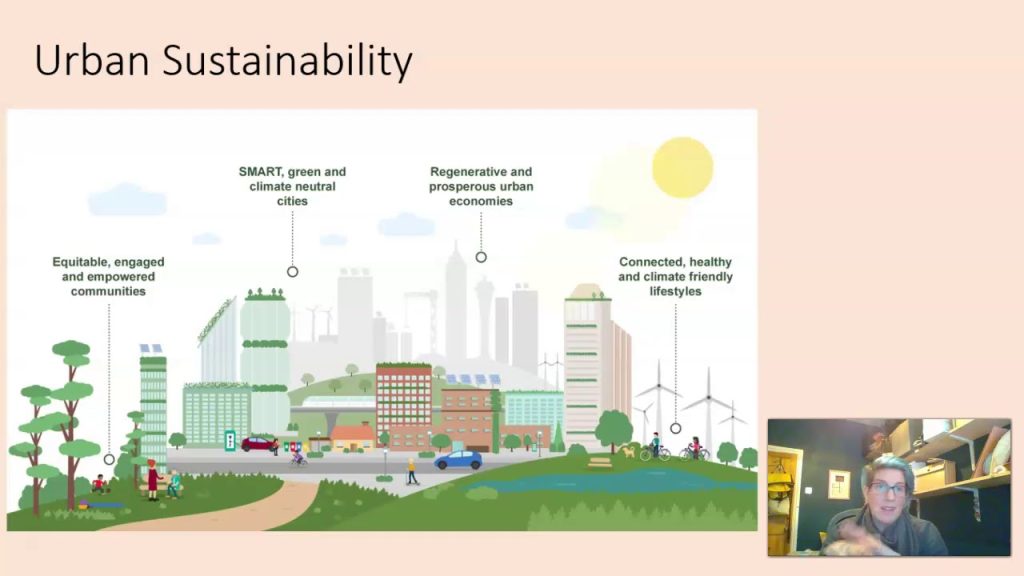
Urban sustainability is the need of the hour, and green infrastructure is an approach that promises to shape urban and suburban landscapes. With rising concerns over pollution in urban areas, water quality, and urban heat island effect, embracing the concept of green infrastructure has become vital. This article will explore different types of green infrastructure that offer multiple benefits, including economic, social, and ecological.
Types of Green Infrastructure for Urban Sustainability
1. Green Roofs
Green roofs are an innovative way to control stormwater runoff and reduce the urban heat island effect. Intensive green roofs can significantly improve insulation, beautify urban landscapes, and contribute to urban greening. Rain that falls on green roofs also helps in water management.
2. Urban Trees and Urban Forest Canopy
The urban tree canopy provides shade, improves air quality, and supports urban ecosystems. Urban forestry plays a crucial role in cooling cities, known as the urban heat effect. They also offer social and economic benefits to urban residents.
3. Green Streets and Green Parking
Green streets are designed with permeable materials and vegetation, aiding in stormwater management and urban heat island reduction. Green parking lots, designed with permeable surfaces, reduce stormwater and enhance urban aesthetics.
4. Blue-Green Infrastructure
Combining both green and water infrastructure, blue-green infrastructure includes features like wetlands and ponds. This innovative approach in urban areas helps in water management, stormwater infrastructure enhancement, and flood control.
5. Urban Green Spaces and Parks
Urban green spaces, parks, and green walls provide recreational areas while also serving vital ecosystem services. These spaces are integral to urban sustainability, enhancing urban environments and offering multiple benefits.
6. Sustainable Urban Planning and Investments in Green Infrastructure
New green infrastructure plans, investments in green infrastructure, and integrating green infrastructure into urban planning can reshape urban landscapes. Whether it’s a large-scale green project or a small urban garden, these practices contribute to sustainable urban growth.
Environmental, Social, and Economic Impacts
Green infrastructure provides environmental benefits by enhancing water quality, reducing pollution, and offering ecological benefits. Moreover, green infrastructure could lead to social benefits like improved public health, while the economic benefits include increased property value.
Future of Green Infrastructure
The development, implementation, and assessment of green infrastructure continue to evolve. With information on green strategies becoming more accessible, urban green infrastructure, and ecosystem service planning are expected to become standard practices.
Different types of green infrastructure, including green walls, multifunctional green spaces, and new green concepts like green parking, are gaining traction. The traditional infrastructure is slowly being replaced by green alternatives, emphasizing the vital role of green infrastructure systems.
Conclusion
Green infrastructure is often seen as the way forward for urban sustainability. From green roofs to green urban planning, these infrastructure elements offer an array of benefits associated with green infrastructure. By understanding the different types of vegetation, infrastructure needs, and the value of green infrastructure, cities can shift towards a sustainable future.
The potential of green infrastructure may seem vast, but its application and effects of green infrastructure can lead to a profound transformation. Embrace the green infrastructure-based solutions for a thriving urban future.