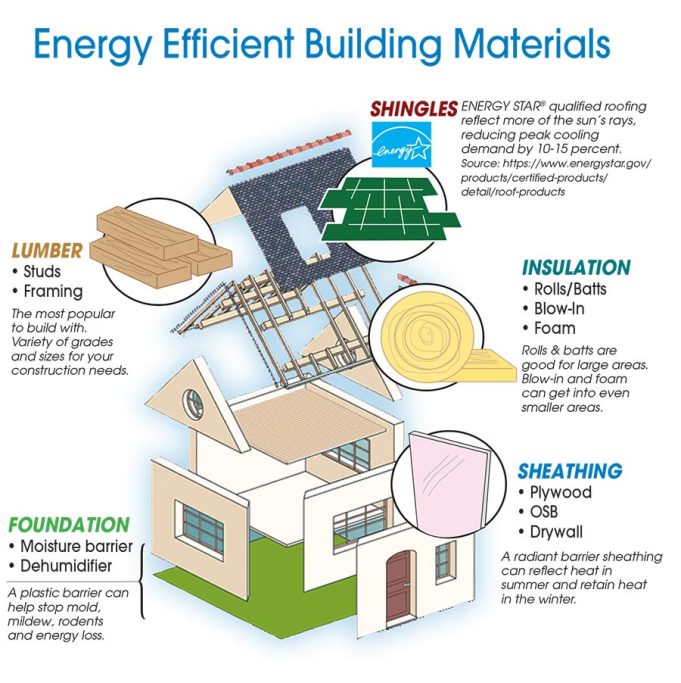
Introduction
In the new construction landscape, energy efficiency is more than just a buzzword; it’s a necessity. With the rising cost of energy and the global shift towards green building, selecting the right materials for thermal insulation is crucial. This article will explore various types of insulation materials, from foam and cellulose to innovative solutions like radiant barriers and reflective insulation systems. Prepare to transform your building into a bastion of energy savings!
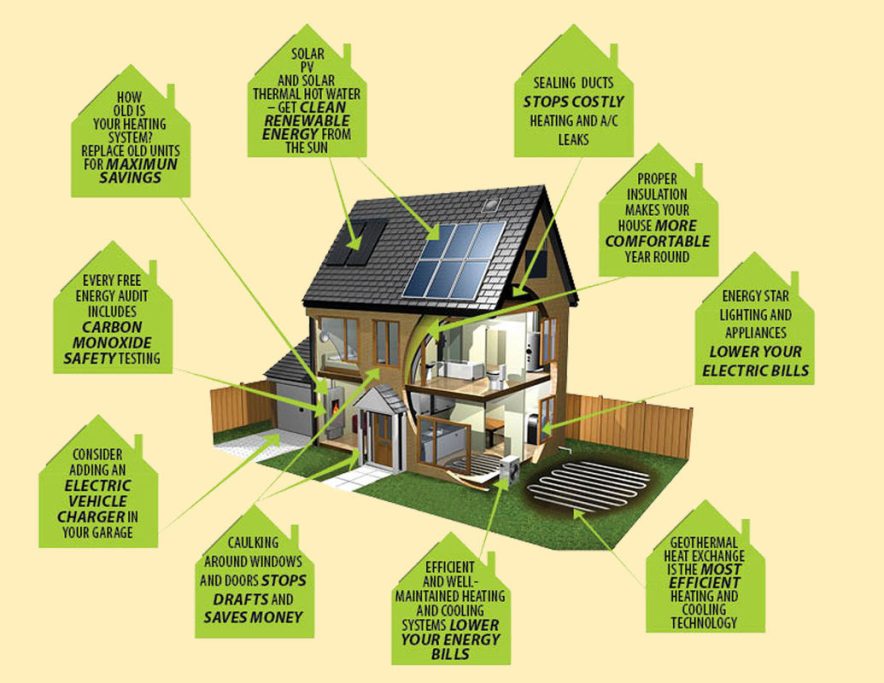
Section 1: The Importance of Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is at the core of the building industry, affecting energy consumption and contributing to a more sustainable future. By utilizing materials with good thermal properties and insulating concrete forms, homeowners can reduce energy use and provide a comfortable environment for building occupants. Key factors to consider include thermal resistance (R-value), thermal conductivity coefficient, and the specific needs of various building components such as walls, ceilings, and roofs.

1.1 Energy Star and Department of Energy Guidelines
The Department of Energy and Energy Star programs provide essential guidelines to improve energy efficiency in both new construction and existing walls. Through these standards, builders and homeowners can make informed decisions on the right materials, such as foam insulation, mineral wool, and expanded polystyrene (EPS) insulation panels.
Section 2: Insulating Materials – A Deep Dive
2.1 Foam and Spray Foam Insulation
Foam materials, including polyurethane foam insulation and spray foam insulation, are widely used to insulate cavities such as walls. Closed-cell foam gives the insulation a spongy texture, offering good sound insulation and excellent thermal performance.
2.2 Fibrous Fiberglass, Rock Wool, and Cellulose Insulation
These materials provide good thermal insulation, with cellulose insulation made from recycled paper products offering an eco-friendly option. Rock wool, in particular, is extremely lightweight and used in many applications, from roof and ceiling insulation to basement walls.
2.3 Radiant Barriers and Reflective Insulation
Radiant barriers and reflective insulation systems act as a vapor barrier and enhance thermal resistance. These materials include aluminum foils and other facing materials that reflect heat transfer, leading to higher R-values and significant energy savings.
2.4 Natural Fibers, Recycled Glass, and Sheep’s Wool
Innovative insulation solutions like natural fibers and insulation made from recycled materials are gaining traction. Sheep’s wool, for example, has good thermal properties, and loose-fill insulation made from recycled glass offers an environmentally conscious choice.
2.5 Insulating Concrete Forms and Concrete Block Insulation
For those looking to build with materials that offer good thermal insulation and energy efficiency, insulating concrete forms and concrete block insulation provide robust solutions. These methods enhance thermal barriers, minimize thermal bridges, and offer versatile design options.
Conclusion
The choice of insulation materials is pivotal to building an energy-efficient structure. From foam board insulation to barriers and reflective insulation systems, the market offers various options. By understanding the R-value, thermal conductivity coefficient, and aligning with guidelines from the Department of Energy, builders can optimize energy usage and contribute to a sustainable building sector.
Investing in the right insulation types, such as spray foam, cellulose, radiant barriers, or even innovative solutions like sheep’s wool, can transform your building, improve thermal performance, and lead to substantial energy savings. Embrace the future of energy efficiency and insulate with intelligence!